3 Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common and serious condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It is caused by the bacteria in plaque, a sticky film that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems. There are different stages of gum disease, each with its own symptoms and treatment options.
Gingivitis
The first stage of gum disease is gingivitis. Gingivitis is a common dental condition that many people experience at some point in their lives. It is characterized by inflammation of the gums caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more serious condition called periodontitis, which could lead to tooth loss.
Causes
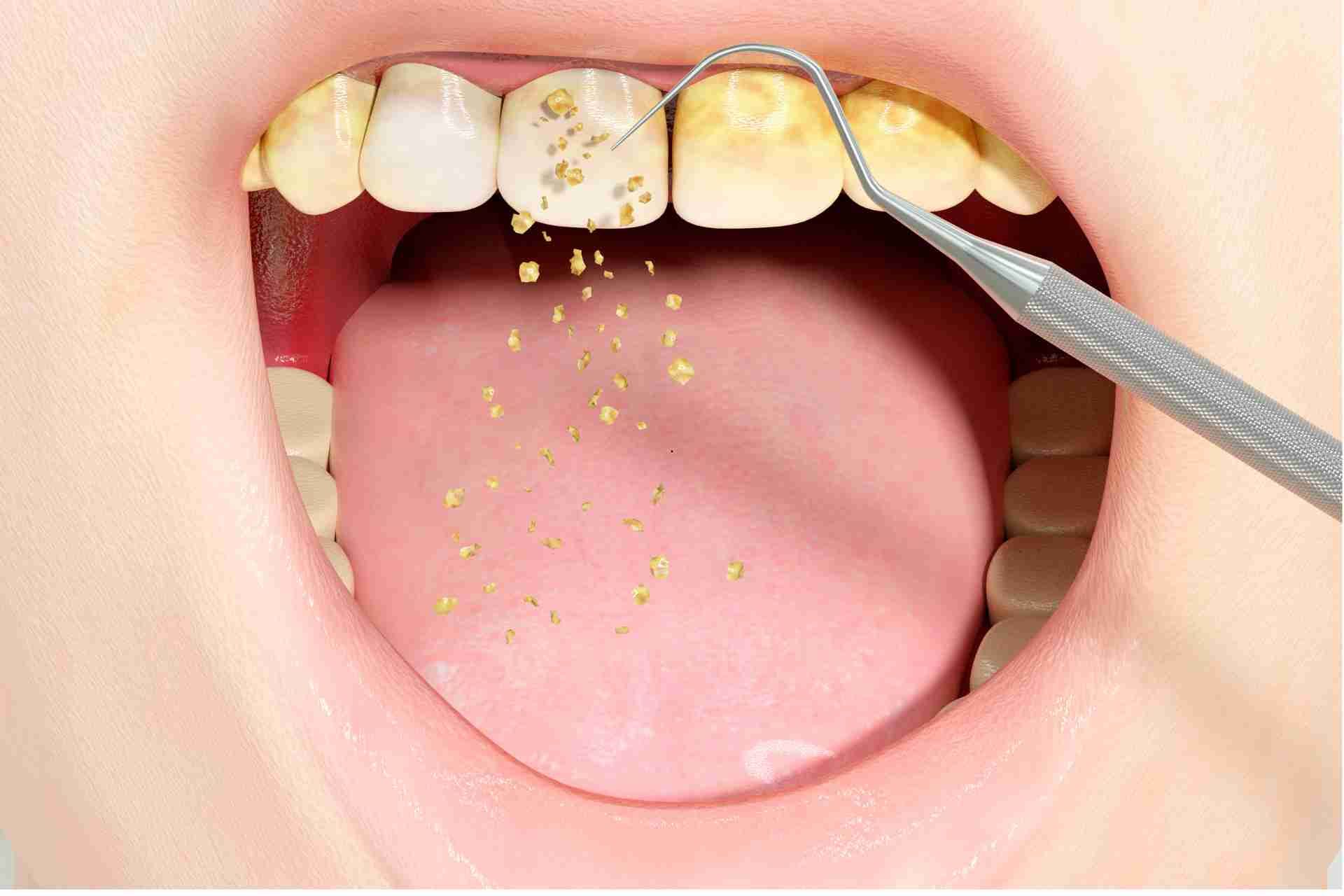
The primary cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene. When plaque builds up on the teeth and along the gumline, it can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation. If the plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning.
Other common causes of gingivitis include:
1. Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
2. Medications: Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives, antihistamines, and some antidepressants, can increase the risk of developing gingivitis.
3. Smoking: Smoking not only weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infection, but it also restricts blood flow to the gums, making it harder for them to heal.
4. Poor nutrition: A diet high in sugary foods and drinks can contribute to the growth of plaque bacteria, while a deficiency in certain nutrients, such as vitamin C, can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infection.
5. Genetics: Some people may be more predisposed to developing gingivitis due to genetic factors that affect the structure of their gums and their immune response.
Symptoms
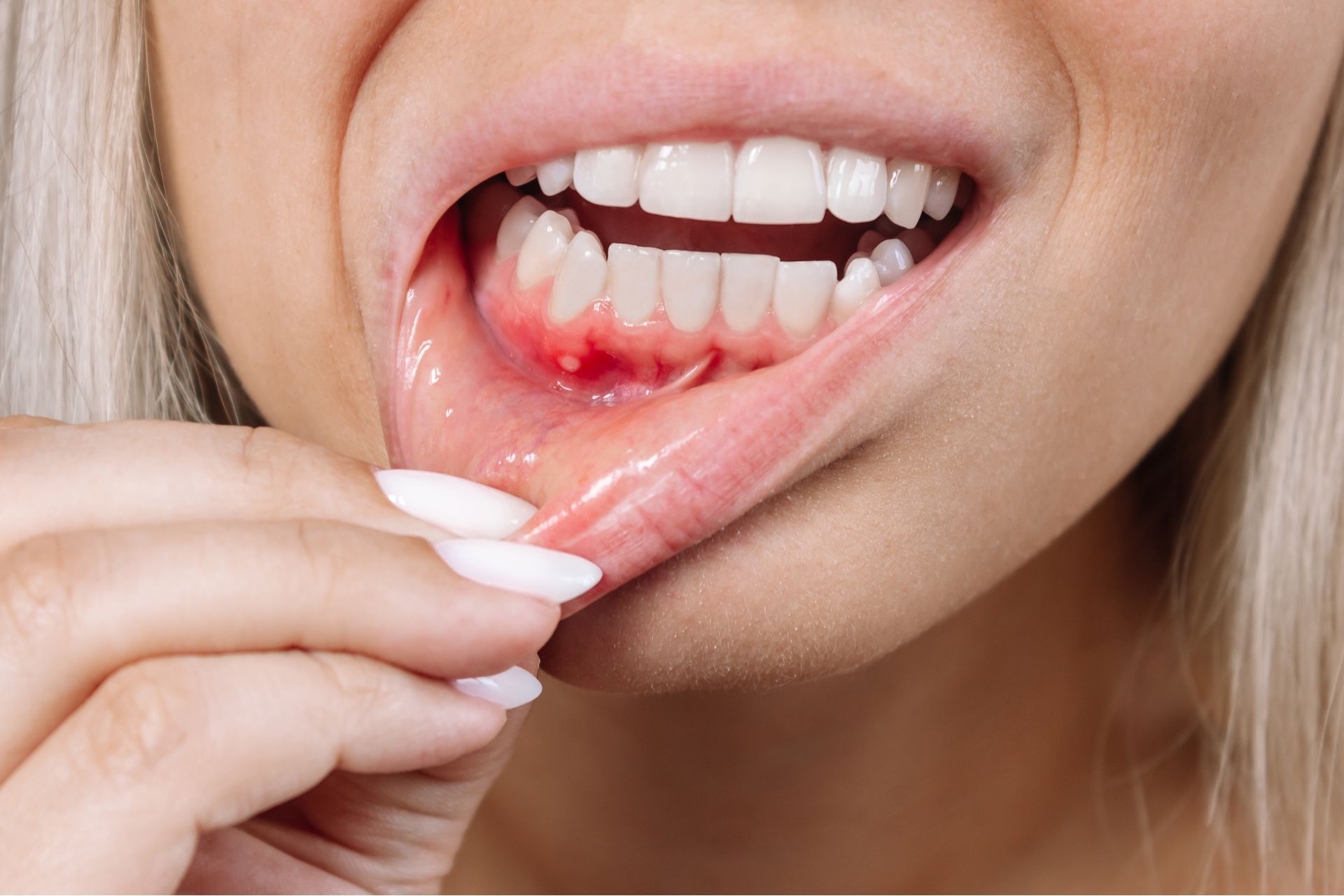
Symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen, and tender gums that bleed easily, especially when brushing or flossing. You may also experience bad breath and a metallic taste in your mouth. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to seek treatment from your dentist as soon as possible.
Treatment
Treatment for gingivitis usually involves improving your oral hygiene habits. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash. Your dentist may also recommend professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup from your teeth.
Periodontitis
The second stage of gum disease is periodontitis. Periodontitis is characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums, as well as damage to the bone and tissues that support the teeth. This stage of gum disease is more severe than the initial stage of gingivitis, and it can cause significant damage to your oral health if not addressed promptly.
If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to a number of serious complications, including tooth loss, receding gums, and even systemic health issues such as heart disease and diabetes. It is important to seek treatment for periodontitis as soon as possible to prevent these complications from occurring.
Causes
Periodontitis is caused by bacteria that build up on your teeth and form plaque, a sticky film that can harden into tartar if not removed by regular brushing and flossing. When tartar accumulates, it creates pockets between your gums and teeth, allowing bacteria to thrive and cause inflammation and infection.
Other risk factors for developing periodontitis include smoking, genetics, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause), poor nutrition, certain medications, and medical conditions like diabetes.
Symptoms
Some common symptoms of periodontitis include:
- Swollen, red, or tender gums
- Gums that bleed easily, especially when brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums or teeth that appear longer
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pain when chewing
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's important to see your dentist as soon as possible for an evaluation and treatment.
Treatment
The good news is that periodontitis can be treated and managed with proper care and attention from your dentist. Treatment options for periodontitis may include:
- Scaling and root planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes tartar and bacteria from beneath the gumline and smooths the roots of the teeth to help prevent bacteria from reattaching.
- Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics, either in the form of pills or mouth rinses, to help combat the infection and reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In more severe cases of periodontitis, surgery may be necessary to repair and regenerate damaged gum and bone tissue.
Advanced Periodontitis
The final stage of gum disease is advanced periodontitis. Advanced periodontitis is characterized by deep pockets of infection and inflammation around the teeth. These pockets can lead to the loss of gum tissue and bone, causing the teeth to become loose and eventually fall out. In addition to tooth loss, advanced periodontitis can also have systemic effects on your overall health. Research has shown that periodontal disease is linked to an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and other serious health conditions.
Causes
Causes of advanced periodontitis can vary, but it is usually the result of poor oral hygiene and inadequate dental care. Plaque buildup, which is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth, can harden into tartar if not removed through regular brushing and flossing. Tartar can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation, eventually causing the gums to pull away from the teeth and form pockets where bacteria can thrive.
Symptoms
Symptoms of advanced periodontitis can include:
- Gum recession
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Persistent bad breath
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Bleeding gums
- Pain when chewing
- Changes in the way teeth fit together
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
Treatment
there are several treatment options available for advanced periodontitis that can help save your teeth and improve the health of your gums. Here are some of the most common advanced periodontitis treatment options:
- Scaling and root planing: This is a deep cleaning procedure that involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and roots of the teeth. This can help reduce inflammation and infection in the gums and promote healing.
- Periodontal surgery: In severe cases of advanced periodontitis, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue and recontour the gums to allow for better cleaning and healing. This can help restore the health of the gums and prevent further damage to the teeth.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy is a minimally invasive treatment option that uses a laser to remove bacteria and infected tissue from the gums. This can help reduce inflammation and promote healing without the need for surgery.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help reduce the infection and inflammation in the gums. These medications can be taken orally or applied directly to the affected area.
- Bone grafting: In cases where advanced periodontitis has led to bone loss around the teeth, a bone graft may be necessary to restore the lost bone and support the teeth. This can help prevent further tooth loss and improve the overall health of the mouth.
It is important to note that advanced periodontitis treatment may require a combination of these treatments to effectively address the issue. Your dentist will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan based on the severity of your condition and your individual needs.
How fast does gum disease progress?
The speed at which gum disease progresses can vary from person to person, depending on a variety of factors. In some cases, gum disease can develop slowly over a period of years, while in others it may progress more rapidly. Some of the factors that can influence the speed at which gum disease progresses include:
Oral hygiene habits: Regular brushing and flossing are essential for preventing gum disease. If you neglect your oral hygiene routine, plaque and tartar can build up quickly, leading to gum disease.
- Genetics: Some people are more genetically predisposed to gum disease than others. If you have a family history of gum disease, you may be more likely to develop it at a faster rate.
- Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease, as it can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infection. Smokers are more likely to develop gum disease and experience its progression at a faster rate.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and autoimmune diseases, can also increase the risk of gum disease and affect its progression.
- Age: As we age, our risk of developing gum disease increases. Older adults may experience a faster progression of gum disease if they do not take proper care of their oral health.
Looking to Prevent a Gum Disease?
One of the best ways to prevent gum disease is by visiting a dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Pennington Orthodontics & Pediatric Dentistry is a leading dental practice that offers preventive care services to help patients maintain optimal oral health.
Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step toward preventing gum disease and maintaining optimal oral health.